A technology for the future
CO2 storage makes good sense
“Carbon capture and storage (CCS) may seem complex, but it doesn’t have to be. We want to give all Danes the opportunity to familiarise themselves with what CCS is. That’s why, together with others in the growing CCS industry, we have created ‘CO2 in depth’, a Danish information portal about CCS”
Ken Wesnæs, CEO
How CCS technology works
CCS technology (carbon capture, transportation and storage) is an advanced process that captures CO2 from industrial emitters and stores it safely and permanently underground. CO2 is stored in suitable geological formations, rather than released into the atmosphere where it would otherwise harm the climate. The technology is crucial to slowing global warming and meeting both Danish and global climate goals. CCS is a sustainable solution that both reduces climate-damaging emissions and contributes to long-term positive effects and new opportunities.

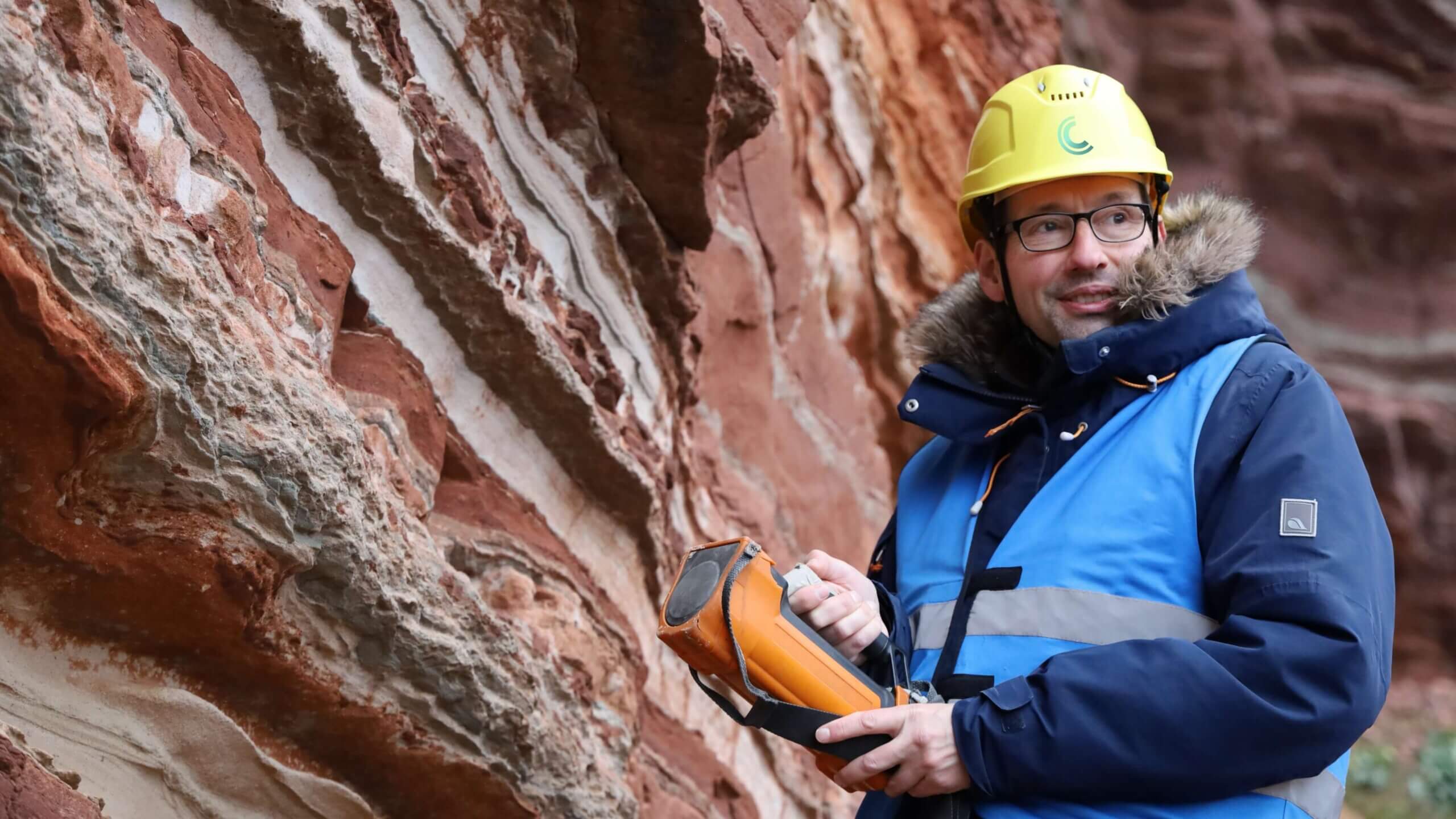
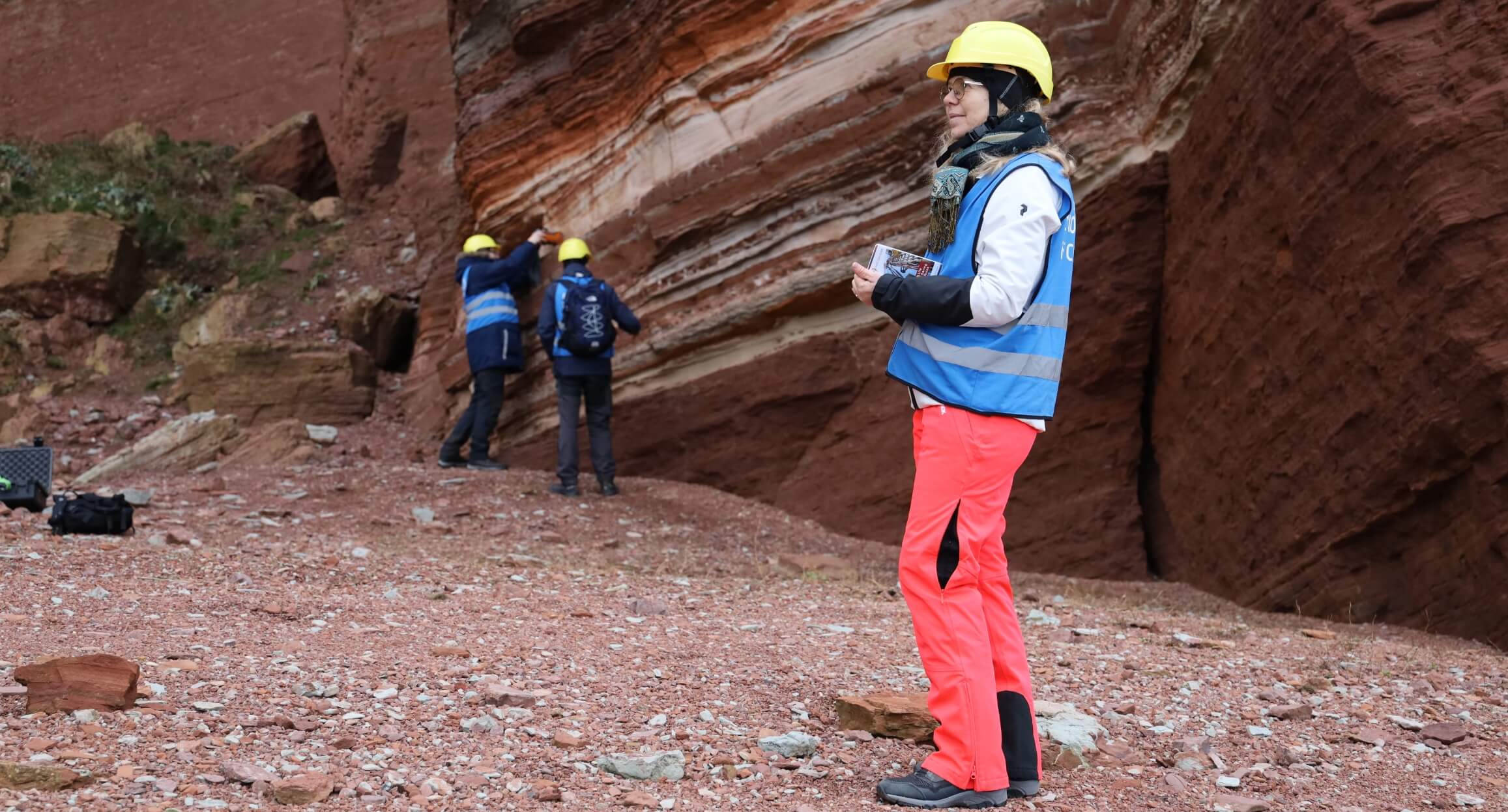
The Ruby Project – a Danish pioneer project in CO2 storage
The Ruby Project is a pioneering project within onshore CO2 storage at Rødby on Lolland. The aim is to develop a safe and permanent CO2 storage deep in the subsoil of South Lolland as part of Denmark’s climate strategy. The project is in the exploration phase and is supported by the authorities with a state exploration license. With Ruby, we combine subsurface expertise, advanced technology, and collaboration in the CCS value chain to create climate impact and economic value. Ruby is owned by BlueNord (80%) and the Danish state via Nordsøfonden (20%).

Ruby Project’s own website
Find more information about the project goals, timeline and technologies on the project website. It has been created to ensure transparency and promote dialog with both local communities and other stakeholders as the project develops.
The value of CCS for the climate fight and the economy
The CCS technology is a key solution in the fight against climate change because it effectively removes and reduces CO2 emissions from industrial processes. The technology is a proven, safe, and scalable method to reduce climate-damaging emissions. With the potential to sequester and store CO2 permanently underground, CCS combines long-term climate benefits with economic returns, making it a future-proof solution.
Safety is our priority
CarbonCuts is in the study phase with Project Ruby – and we are not yet storing CO₂. If our studies show that it will be possible, we will always use the most advanced monitoring technologies and geological analysis methods to ensure that storage takes place safely and under fully controlled conditions. We work with authorities and experts to guarantee that all safety standards are met and that our activities do not pose a risk to people or the environment.
CCS is a climate technology with multiple options
The CCS technology is prioritised by the Danish government and is emerging globally as a key climate solution. Carbon capture and storage plays a key role in meeting global climate goals. At CarbonCuts, we are committed to developing safe and efficient solutions for carbon management and storage should Ruby be realised. At the same time, we are exploring opportunities for collaboration on the management and utilisation of CO₂ that can, for example, be used for the production of electro-fuels through Power-to-X technology.